A RECOGNIZED METHOD…
WITH A COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE REFERENCE STANDARD
A RECOGNIZED METHOD...
- DMAC is a validated method for measuring total soluble PACs in cranberry and can be used by any lab worldwide. Use of this single method reduces variability in results among different labs.
- The first publication of the DMAC assay’s SOP (standard operational procedure) was in 2010 (Prior et al). The method was developed by Brunswick Laboratories, hence the prefix “BL-DMAC” method
- In 2017, AOAC published the SOP of the improved and single-validated ICT/DMAC/A2 method by ICT Labs, in which the overall RSD (relative standard deviation) was reduced from 16.5 % (BL-DMAC) to maximum 5% (Sintara et al. 2018)
- The Standardized ICT/DMAC/A2 method will be part of the upcoming USP (US Pharmacopoeia) Monographs for Cranberry Fruit Juice Dry Extracts and for Cranberry Fruit Juice Concentrate.
- Previously, the ICT/DMAC/A2 method’s detailed SOPs were also published in the Cranberry MONOGRAPH of the American Herbal Pharmacopoeia (AHP). (Upton and Brendler 2016)
...WITH A COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE REFERENCE STANDARD
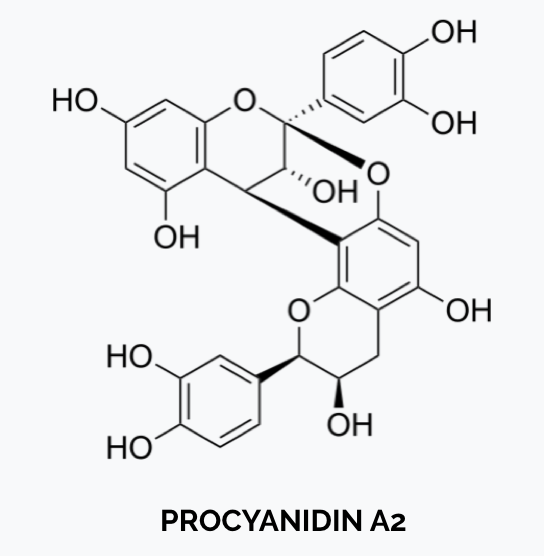
- For worldwide industry use and product comparative purposes, reference standards should be commercially available to allow the method to be performed in multiple labs.
- Certain labs use proprietary, not commercially available “cPAC standards” derived from oligomeric PAC, which are better able to measure the larger PACs in cranberry.
In that case, the use of such proprietary standard should be clearly listed on product labels. - DMAC uses a commercially available dimeric Procyanidin A2 reference standard, which should always be used for comparing PAC levels in cranberry products.
- This standard had already been used in the SOPs in the first publication of the DMAC method (Prior et al., 2010) and also in the improved SOPs of ICT Labs, published by AOAC in 2017.
